Ukraine plans to deliver world’s largest jet to China
KIEV — Ukraine said on Wednesday (Sept 7) it may deliver the world’s largest jet — originally developed for the Soviet Union’s abandoned space shuttle programme — to China within the next five years.
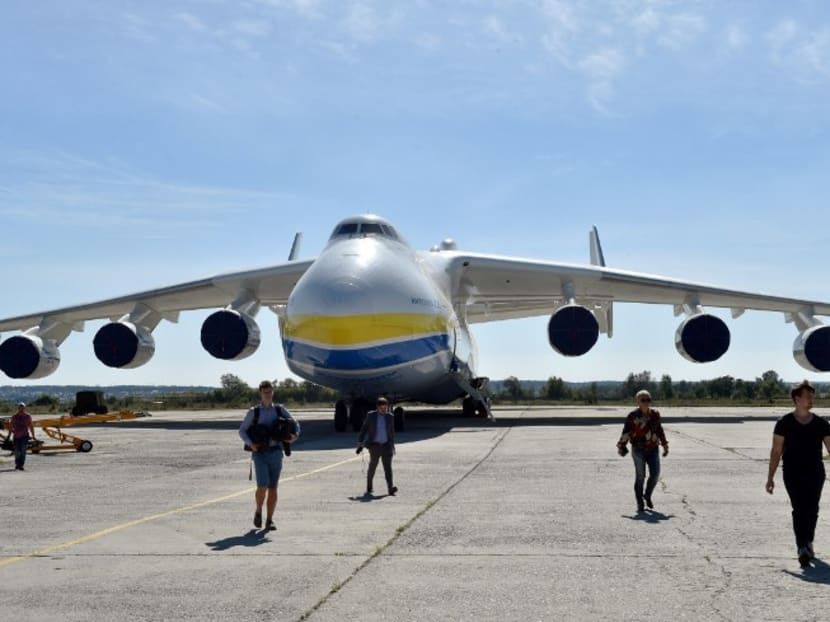

An Antonov-225 Mriya plane is seen at Antonov plant's airdrome Gostomel, some 30 km from Kiev during press-tour on September 8, 2016. Photo: AFP
KIEV — Ukraine said on Wednesday (Sept 7) it may deliver the world’s largest jet — originally developed for the Soviet Union’s abandoned space shuttle programme — to China within the next five years.
The first AN-225 Mriya (Dream) six-engine heavy lifter was built by the Antonov aircraft maker in the 1980s.
The company moved in 1952 from Siberia to Kiev and then fell into Ukraine’s lap when the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991.
Antonov and the Aviation Industry Corporation of China signed a memorandum of understanding on August 30 to renew the plane’s production in China under licence from Ukraine.
The only functioning Mriya jet last completed a large cargo delivery from the Czech Republic to Australia in May.
A second jet was only partially finished and has remained in Ukrainian storage for the past 28 years.
Antonov’s China project coordinator Gennadiy Gabruk said the second plane would be fully upgraded and “under optimal conditions” delivered to China by 2021.
“This jet will be built using the basis of the basic framework we already have, but all the equipment will be new,” Mr Gabruk told reporters.
The memorandum of understanding foresees mass production of the Mriya by China under Antonov’s licence if all the technical details are resolved.
China reportedly conducted covert work on its own shuttle programme before dropping the idea in the 1990s.
But the booming nation is keen to join the international space race and is reportedly considering a permanently manned moon base.
Such a project would need a vessel to transport people to and from Earth.
The Soviet Union developed the Mriya to help lift off shuttles that could compete against those being used by the United States.
Moscow conducted a successful test flight of an unmanned Buran orbiter from its Baikonur space centre in present-day Kazakhstan in 1988.
The Mriya was able to ferry the Buran fixed on top of the plane.
But a second flight planned for the early 1990s had to be scrapped because of the Soviet Union’s disintegration and Russia’s subsequent deep economic malaise.
China has not officially said what plans it has for the plane.
Some military experts believe that Beijing does not intend to employ the Mriya in a space programme but rather to use it as a heavy lifter for domestic and international projects.
RUSSIA SPAT
Ties between Kiev and Moscow have been frozen since Russia in March 2014 seized Crimea after swarming the Ukrainian peninsula with troops and then overseeing an independence referendum the UN General Assembly condemned as “illegal”.
Russia now denies backing a pro-Kremlin revolt that broke out in the east of Ukraine in the following weeks.
The 28-month war has claimed nearly 9,600 lives and resulted in Ukraine cancelling major aviation projects with Russia.
The former Soviet republic currently refuses to service the world’s largest mass-produced cargo jet — the An-124-100 Ruslan that Russia flies around the world for emergency relief and contracted work.
Antonov’s chief Oleksandr Kotsyuba said in a statement that Ukraine could no longer be held liable for the safety of Russia’s Ruslan jets. AFP