Alarm as Greenland ice sheet sheds half-a-trillion tonnes
PARIS — Greenland's massive ice sheet saw a record net loss of 532 billion tonnes last year, raising red flags about accelerating sea level rise, according to findings released Thursday (Aug 21).
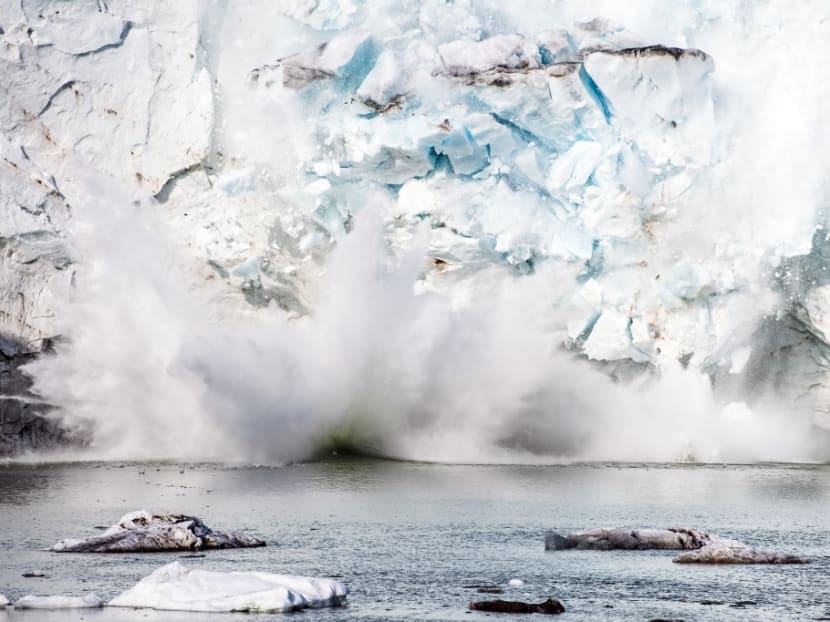

An iceberg calving with a mass of ice breaking away from the Apusiajik glacier, near Kulusuk, a settlement in the Sermersooq municipality located on the island of the same name on the southeastern shore of Greenland.
PARIS — Greenland's massive ice sheet saw a record net loss of 532 billion tonnes last year, raising red flags about accelerating sea level rise, according to findings released Thursday (Aug 20).
That is equivalent to an additional three million tonnes of water streaming into global oceans every day, or six Olympic pools every second.
Crumbling glaciers and torrents of melt-water slicing through Greenland's two-to-three-kilometre thick ice block were the single biggest source of global sea level rise in 2019, accounted for 40 per cent of the total, or 1.5 millimetres, researchers reported in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.
Last year's loss of mass was at least 15 percent above the previous record in 2012, but even more alarming are the long-term trends, they said.
"2019 and the four other record-loss years have all occurred in the last decade," lead author Ingo Sasgen, a glaciologist at the Helmholtze Centre for Polar and Marine Research in Germany, told AFP.
If all of Greenland's ice sheet were to melt, it would lift global oceans by seven metres.
Even a more modest rise of a couple of metres would redraw the world's coastlines and render land occupied today by hundreds of millions of people uninhabitable.
Until 2000, Greenland's ice sheet — covering an area three times the size of France — generally accumulated as much mass as it shed.
Runoff, in other words, was compensated by fresh snowfall.
But over the last two decades ago, the gathering pace of global warming has upended this balance.
The gap is widening at both ends, according to the study, which draws from nearly 20 years of satellite data.
Changing weather patterns — also a consequence of climate change — has resulted in less cloud cover, and thus less snow. These high pressure systems have also resulted in more, and warmer, sunny days, accelerating the loss of mass.
CLIMATE SYSTEM 'TIPPING POINT'
In 2019, the ice sheet lost a total of 1.13 trillion tonnes, about 45 per cent from glaciers sliding into the sea, and 55 per cent from melted ice, said Mr Sasgen. It gained about 600 billion tonnes through precipitation.
A study in the same journal last week concluded that the Greenland's ice sheet has passed a "tipping point", and is now doomed to disintegrate, though on what time scale is unknown.
Mr Sasgen says it is too soon to know if we have reached a point of no return, but agrees that the ice sheet is likely to continue losing mass, even in colder years.
"But that doesn't mean that trying to limit warming doesn't matter," he added.
"Every decimal degree you save in terms of warming will save a certain amount of sea level rise — both in magnitude and speed."
Experts not involved in the research were not surprised by the findings, but expressed concern nonetheless.
"The ice sheet has lost ice every year for the last 20 years," said Ms Twila Moon, a research scientists at the University of Colorado.
"If everyone's alarm bells were not already ringing, they must be now."
Mr Stuart Cunningham, an oceanographer from the Scottish Association for Marine Science, warned about the potential impact on the North Atlantic circulation, a current that keeps northwestern Europe five to ten degrees Celsius warmer that similar latitudes elsewhere on the globe.
"Climate models show this circulation can be switched off by adding fresh water to the North Atlantic," he said, noting this happened during the end of the last ice age.
"This tipping point in the climate system is one of the potential disasters facing us."
From 1992 to 2018, Greenland lost about four trillion tonnes of mass, causing the mean sea level to rise by 11 millimetres, according to a December 2019 study in Nature. AFP