The Big Read in short: The rise of TikTok and its profound impact on society
SINGAPORE — Driven to “insanity and boredom” while being stuck at home during the partial lockdown in 2020, Ms Nicole Liel turned to a new social media app that her social circle has been using to pass her time.
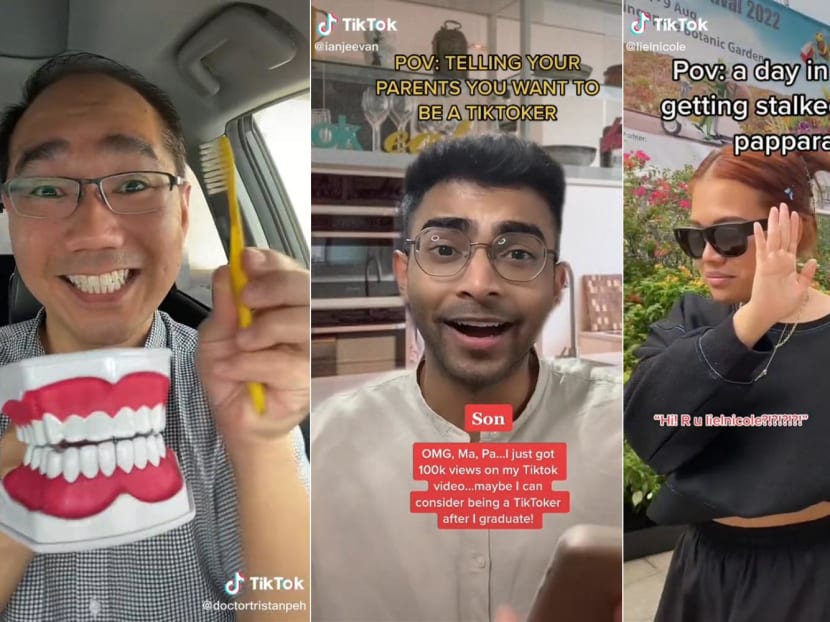
(L-R) TikTokers Tristan Peh, Ian Jeevan Prasad Arumugam and Nicole Liel.
Each week, TODAY’s long-running Big Read series delves into the trends and issues that matter. This week, we examine TikTok's meteoric rise around the world including in Singapore, and the impact on society. This is a shortened version of the full feature, which can be found here.
- While mobile application TikTok was already gaining popularity around the world, the Covid-19 pandemic has turbocharged its growth as a social media platform over the last two years
- As a result, rivals such as Facebook are struggling to play catch-up and incorporate features that mimic the mobile app developed by Chinese tech firm ByteDance
- As TikTok introduces features to commercialise the platform, some Singapore TikTok creators — or 'TikTokers' — have found ways to monetise their fame
- Experts noted the powers of TikTok in helping ordinary people achieve fame and fortune or amplify social causes, as well as allowing smaller, less visible communities to band together
- At the same time, there is a whole range of concerns about its negative impact, especially on younger users, including addiction and other mental health issues
SINGAPORE — Driven to “insanity and boredom” while being stuck at home during the partial Covid-19 lockdown in April 2020, Ms Nicole Liel turned to a social media app that was fast gaining popularity among her friends — and around the world — as a way to pass time and be entertained.
The mobile application, TikTok, allowed her to watch and create her own short-form videos.
“I thought I’d (have fun) and post some videos. I woke up the next day, and my phone was just blowing up with notifications…Every time I refreshed my TikTok profile, I would just see the viewer numbers increasing in the thousands per minute,” the 24-year-old recounted to TODAY.
Two years on, Ms Liel, a self-professed full-time "TikToker", boasts more than 125,000 followers and has amassed over 10 million "likes" for her videos, which range from skits reimagining Stamford Raffles in modern Singapore, to product reviews and vignettes of her daily life.
For someone who had toyed with the idea of being an entertainer when she was younger, the app has opened the door for Ms Liel to earn a living as one, as she began getting requests to do sponsored posts for brands earlier this year.
She estimates that she earns, on average, “higher than a fresh graduate’s salary” of S$3,000 a month.
Her TikTok journey echoes that of many others who have shot to fame — both in Singapore and overseas — from posting short, quirky videos on the app.

Social media experts told TODAY that while TikTok was already gaining traction when it launched internationally in 2017, it was boredom and isolation at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic that boosted the take-up rate of the Chinese mobile app around the world.
According to market intelligence firm Sensor Tower, global downloads of the app surged from 200 million in the last quarter of 2019 to more than 300 million in the first three months of 2020, when the pandemic saw consumers “drawn to their mobile devices more than ever”.
TikTok’s rapid rise has also forced its competitors, particularly Facebook, to play catch-up and introduce features that mimic those of the former.
In late July, Facebook tweaked its algorithm so that people scrolling through its home page can discover content that is “uniquely personalised to them”, said Meta, its parent company, in a blog post.
This means that users will not only see posts from accounts that they follow, but also content from accounts that they do not.
This is similar to how TikTok’s algorithm recommends content based on users’ interests, rather than which accounts they follow.
How Covid-19 turbocharged TikTok's global rise
TikTok, which allows users to edit and share short-form videos, is the brainchild of Chinese tech company ByteDance.
It was first launched in China in 2016 as the Douyin app, before it was launched internationally a year later as TikTok.
But it was the US$1 billion acquisition in 2017 of another Chinese application, Musical.ly, that shot TikTok to global prominence. Musical.ly allowed users to lip-synch to popular songs and dance.
The deal gave TikTok access to the Musical.ly’s 80 million users who were mostly based in the United States.
Following the acquisition, TikTok’s rise was meteoric: By 2020, it had knocked Facebook messenger off top spot as the most downloaded application globally, according to market tracker data.ai.
Data from the market analysis company Business of Apps also showed that TikTok generated US$4.6 billion in revenue last year, which translated to a 142-per-cent increase in revenue year-on-year.
While Facebook’s revenue last year was US$118 billion, its year-on-year growth was 37 per cent.
Likewise, the number of users on Facebook has been stagnating, stalling for the first time at 2.9 billion monthly active users in the fourth quarter of last year.
Meanwhile, TikTok’s number of monthly active users grew from 7.6 million to 1.2 billion during the same period. A majority of its users are under the age of 30, and come from China, the US, Indonesia and Brazil.
Experts attributed TikTok’s rise globally to its unique algorithm, which unlike other social media apps, takes “centrestage” in the mobile application.
“(The app) successfully reads user preferences and suggests ‘perfect’ content. It also provides a wider reach for content generators because the algorithms prioritise content over the number of followers a user may have,” said Assistant Professor Saifuddin Ahmed from the Nanyang Technological University’s Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information.
It was also a matter of timing, said Professor Lim Sun Sun, who heads the Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences at the Singapore University of Technology and Design.
While TikTok already had its fans pre-Covid-19, it was only during the pandemic that the app “took off”, she said.
The app encouraged participatory engagement, such as dance challenges, more so than Facebook or Instagram and brought families and groups of friends together via such activities.
At a time when people were often isolated due to on-off lockdowns, TikTok had the edge over other social media platforms because it gave people the ability to bond with fun elements, Prof Lim said.
TIKTOK'S GROWTH IN SINGAPORE
In Singapore, a survey found that TikTok made “significant gains” in the number of users in the last two years as the pandemic raged.
The survey was conducted by the Centre for Information Integrity and the Internet at the Nanyang Technological University's Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information (WKWSCI).
Some 13.6 per cent of the survey participants said they used TikTok in December 2020, compared with 25.3 per cent saying they did so a year later.
The survey, which is conducted nation-wide every half yearly, involved more than 400 respondents who participated in three surveys in December 2020, July 2021 and December 2021.
In response to TODAY's queries, a TikTok spokesperson from Singapore said that "it was only natural" for online platforms such as TikTok to see an increase in user activity during the pandemic when more people stayed at home.
"We've also seen this increase in TikTok user activity continue even as restrictions eased in Singapore — leading to the platform surpassing 1 billion active global users monthly in September 2021," added the spokesperson.
LIVING OFF THE TIKTOK DREAM AND THE PRESSURE TO STAY RELEVANT
As TikTok’s popularity grows globally, so has its efforts to move beyond being a platform for trendy dance sequences — to one which promotes commerce.
To allow TikTokers to monetise their fame, the app has launched several features, including TikTok Creator Marketplace and TikTok Live in 2019.
In May this year, TikTok also introduced a subscription service for its TikTok Live where content creators can generate recurring revenue from fans through additional perks such as subscriber-only chats.
All seven TikTokers whom TODAY interviewed said that they have made money from participating in brand sponsorships or publicising services on the platform.
Ms Liel said that the rates for branded TikTok videos are usually in the range of thousands of dollars. Her highest-paid project on TikTok was a “five-figure number” while her least lucrative projects are usually in exchange for the products that she is promoting.
While her monthly earnings are sometimes higher than that of a fresh graduate, Ms Liel acknowledged that what she does on TikTok cannot provide a stable income source.
“I can be rolling in dough when big projects (involving large sums of money) come in one month, and then become a pauper the next month,” she quipped.
To this end, Ms Liel said she has set up her own business — she runs several eyelash studio outlets — to ensure that she has something to fall back on if she becomes irrelevant and unable to make money on TikTok.
Another TikToker, dentist Tristan Peh, also started off by doing videos during the early part of the pandemic in March 2020 to bond with his young daughters, who were aged 6 and 9 then.
Dr Peh, 43, who has gained more than two million followers through his videos on dental hygiene, said that he constantly gets emails from brands looking to do sponsored posts for toothbrushes or water flossers.
He began receiving requests for sponsored posts about four to five months after he started posting videos on TikTok.
He charges around US$5,000 (S$6,856) to US$10,000 for each post, based on his study of the market rates for such collaborations.
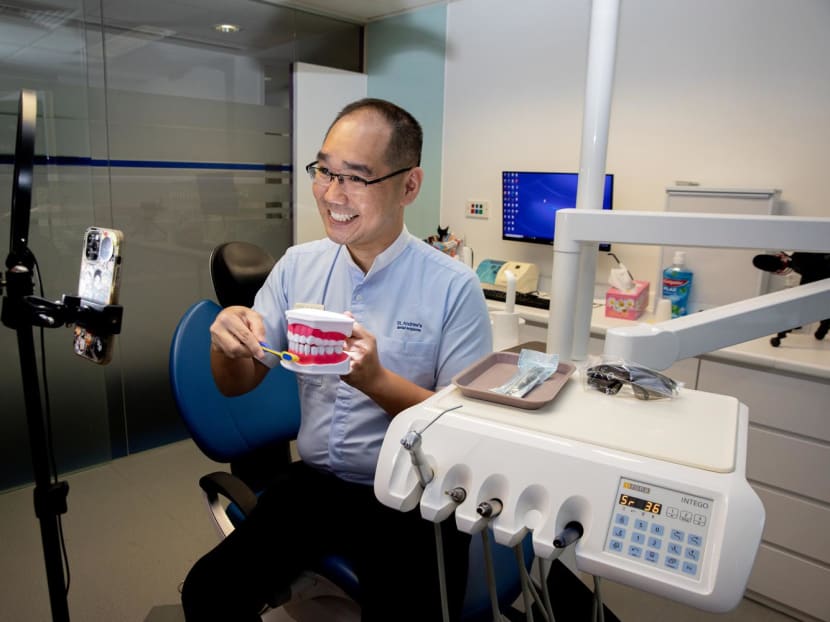

However, Dr Peh said that he is “not really into sales” and is mostly on TikTok to “just have some fun, spread awareness (on dental hygiene) and get everyone to smile”.
For some of these content creators, there is the fear of losing their relevance in a space where the audience's taste is fickle and constantly evolving.
Ms Liel said: “My worry is about whether I can start a family with a job that can be taken away (just) like that. It’s (like) the whole world could collectively decide that they don’t need you and I know that’s imminent, because unless you create drama every day (on social media), you’ll become irrelevant.”
“It’s (like) the whole world could collectively decide that they don’t need you... because unless you create drama every day (on social media), you’ll become irrelevant.TikToker Nicole Liel, 24, who has more than 125,000 followers and has amassed over 10 million "likes" for her videos”
Nevertheless, other TikTokers said they do not see the need to chase “likes” or boost follower count because they feel financially secure with their day job.
One of them, Mr Hafidz Rahman, a 33-year-old arts educator, said: “I do content when I want it and I’m quite comfortable doing it at my own pace. In terms of finding followers, I think they will come at their own time.”
Mr Hafidz, who has been producing content on social media platforms since 2014, has 103,000 followers on TikTok and is known for playing the role of a Malay lady in comedy skits.

THE GOOD AND BAD OF TIKTOK
The TikTokers interviewed cited the ease of the app's video editing features and diverse reach as major draws for them.
Mr Cavin Chua Kar Shin, a 22-year-old university student who has been making videos on YouTube since primary school, said that TikTok allows anyone to build a following without needing to look good or have a following on other social media platforms first.
“For YouTube, for instance, it takes very long to build a following, but you can do it really quickly on TikTok. Anyone can make a video and have it appear on the ‘For You Page’ at any time,” he said.
The third-year communications and new media student at the National University of Singapore has more than 180,000 followers on his TikTok account cayydences. His posts range from comedy skits, to anecdotes about his daily life.
Other upsides of the platform cited by the TikTokers include the sense of community it provides, and the opportunities to produce educational content or present minority views.
Still, there are also drawbacks from being a TikTok personality, said those interviewed, with some lamenting the loss of their privacy.
Recalling how someone had interrupted his date for a photo request recently, Mr Chua said that he tries not to leave his house as far as possible and sticks to areas with fewer people to avoid being approached or recognised on the streets.
The TikTokers also cited hate comments as another hazard they have to face. As it is fairly easy to sign up for a TikTok account and remain anonymous on the platform, the problem is exacerbated on TikTok compared with other social media platforms, they said.
The TikTok spokesperson said that the company “does not tolerate bullying on its platform” and have developed several safeguards against it.
These include the removal of comments that go against TikTok’s community guidelines, such as those which involve harassment or bullying, and hate speech.
TikTok has also partnered with digital safety organisations in Singapore such as the Media Literacy Council to launch campaigns that prompt users to think before they post or comment on videos.
EXPERTS ON THE DOUBLE-EDGED IMPACT OF TIKTOK'S RISE
As with all other social media platforms, TikTok comes with the good, bad and ugly, said experts.
On the plus side, Professor Lim Sun Sun from the Singapore University of Technology and Design highlighted how TikTok — with its ability to let anyone broadcast themselves — allows smaller, less visible communities, such as those with medical conditions, to band together.
It has also given regular folks with seemingly mundane lives an avenue to become famous, unlike influencers on other platforms such as Instagram, which is usually associated with glitz and glamour, said Prof Lim. She cited the example of how Mr Raymond Lim, better known as Uncle Raymond, had risen to fame by broadcasting his dances outside MRT stations on TikTok.
Despite its upsides, TikTok has also received its fair share of criticism.
WKWSCI Assistant Professor Saifuddin Ahmed noted that there have been more widespread discussions surrounding censorship, privacy, and surveillance on TikTok compared with other social media platforms, although these issues are not necessarily specific to TikTok.
This is due to allegations of data mishandling and TikTok bowing to pressures from the Chinese government on how the data is used, he said.
Prof Lim also raised concerns about how TikTok’s algorithm has been designed to keep users on the platform longer, generating the fear that its algorithm could draw users into harmful content such as reckless and risky acts, eating disorders or substance abuse.
TikTok said that its recommendation system, the For You feed, is central to the TikTok experience. Recommendations are based on several factors including user interactions, video information and device and account settings.
Its spokesperson added that TikTok is aware that one of the "inherent challenges" of recommendation engines is that they can "inadvertently limit (a user's) experience" sometimes referred to as a filter bubble.
“We recognise these concerns, and continue to strike a balance with optimising our For You feed for personalisation and relevance, while also helping users find fresh content and uncover new creators,” said the spokesperson.
The spokesperson added that while safety is at the heart of the recommendation system, that did not mean that serious or controversial content did not have a place on the platform, which is ultimately built to support users’ diverse thoughts, experiences and interests.
'THE MOST ADDICTIVE' SOCIAL MEDIA APP
The success of TikTok's algorithm has led to it being dubbed the "most addictive" social media app. But its very strength is what could cause the most harm to users.
Mr John Shepherd Lim, chief well-being officer of Singapore Counselling Centre, said that the excessive use of TikTok is “undoubtedly a common contributing factor” to the mental health concerns that its young clients face today.
TikTok’s continuous supply of entertaining content and the “rapid-fire nature” of its videos train viewers’ minds to quickly assess how pleasurable content is during the first few seconds. This may lead to a shortened attention span and a judgmental attitude that users can bring into other aspects of their lives, such as school or work, he noted.
“If we seem to be performing other tasks at our normal capacity, our TikTok usage should not be a concern. Otherwise, users could consider setting a daily limit on TikTok screen time through the app’s settings.Mr John Shepherd Lim, chief well-being officer of Singapore Counselling Centre”
“A litmus test for how affected our attention spans are, is to measure the length of time it takes for us to get impatient with less-pleasurable activities, such as homework," said Mr Lim.
"If we seem to be performing other tasks at our normal capacity, our TikTok usage should not be a concern. Otherwise, users could consider setting a daily limit on TikTok screen time through the app’s settings."
The TikTok spokesperson said it has options for users to manage the time spent on TikTok, including the daily limit feature which Mr Lim referred to.
The spokesperson reiterated that it is committed to protecting the safety of young users and has designed tools and strategies to prioritise age-appropriate experiences. These include community guidelines that prohibit nudity, pornography or sexually explicit content on TikTok.
The spokesperson said that TikTok also recognises that some content may contain mature or complex themes intended for older audiences. It is building a new system that will allocate maturity level to videos which will be rolled out in the coming months.
“Our users' well-being remains our top priority and there is no end to our work on this front. As such, we are committed to actively developing and reinforcing our safety features to continue cultivating healthy digital practices and positive online experiences,” said the spokesperson.